What’s the difference between bass reflex vs acoustic suspension? Though both enclosures perform well, a lot has been done to improve efficiency over the years.
All loudspeaker and sound system manufacturers face various challenges when crafting high-quality products that match your expectations. From box design to calculating the number of vents to put on your ported system to bass reflex port tuning, these are just a few issues to mention. But there’s more. The frequency response and differences in sound pressure levels have to be scientifically balanced for an optimum experience. Factors such as resonance frequencies and the pressure difference between the speaker’s internal components and the environment are crucial to your system’s overall performance.
Whether you’re new to car audio or have much more experience building your own systems, achieving minimal distortion at optimum performance is everyone’s dream. But to get there, you have to get the perfect combination of bass, mid and high frequency in all kinds of enclosures. In this article, Audio Curious looks deeper into two of the most common loudspeaker enclosures, pros & cons, and their differences to help you make an informed decision.
Types Loudspeaker Enclosures
Loudspeaker enclosures exist in various forms. We have the front and rear-loaded horn, the passive radiator, the transmission line (or labyrinth), the tapered tube, and the two most popular enclosures; the bass reflex (vented/ported) and acoustic suspension speaker systems. What’s unique about all these speakers is their ability to overcome distortion, play optimally at varying sound pressure, and overcome other issues such as volume and accuracy through their designs.
Today, the bass reflex speaker design remains the most popular enclosure, although the acoustic suspension enclosure design is not far off. But what are the differences between these two? Are acoustic speakers the better choice, or are bass reflex speakers better? To understand this, you need to look further into how they both work.
What Is a Bass Reflex Speaker?
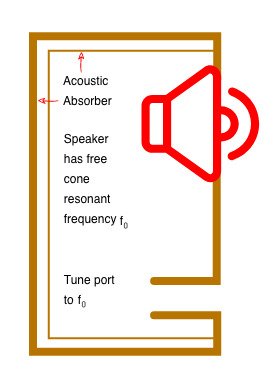
In layman’s language, a bass reflex speaker has a hole drilled into the cabinet. It has a free cone resonant frequency. Bass reflex speakers are some of the most common speakers you’ll see from big brands like Pioneer, Sony, SayonApps, Kenwood, and Samsung, among others.
Back in the day, bass reflex speaker designs were made in a trial and error process. This went on for years until finally, two brilliant minds, A.N.Thiele and Richard H, discovered how to determine the driver’s performance in any enclosure mathematically. They had found the relationship between the speaker itself and its enclosure. Today, these formulas are used to find the electromechanical parameters that define the speaker’s performance in a particular enclosure.
For example, the formula Vb=(15)(Vas)(Qt2.87) is widely applied in calculating the preferable box size. It takes into account the volume of the box (Vb), a constant (15), equivalent driver compliance (Vas), and Qts. Check out other related Thiele/Small parameters.
Highly efficient speakers have relatively high free air resonance (Fs) drivers. When sealed in a box, these drivers tend to experience what we call a high system resonance. This negatively affects the system’s decent bass response. Remember, the resonant frequency for a bass driver should be as low as possible to bring out the bass as accurately.
The other feature that makes the bass reflex good at its job is the port at one side of the enclosure. When the speaker plays music, it generates a front wave and a back wave from the opposite side. The port inverts the back waves so that they can be in phase with the front waves.
Unfortunately, even the most advanced bass reflex speakers have a downside. They face turbulence and vortex shedding problems at the ports. Sound tends to create turbulence when exiting through the port. But the good news is that manufacturers have found a solution through flared ports instead of straight ports. Research shows that optimally flared ports can be played 1 to 3 dB louder than under flared or over flared ports. They can also be played about 10dB louder than straight ports.
Bass Reflex Pros
- Improved bass output
- Better overall performance
- Users can enjoy better bass at higher power
- It does not necessarily need an amp to produce good quality bass
Bass Reflex Cons
- As the lower frequency approaches port resonance, it gets more difficult to get a decent linear response
- Port noise especially at higher volumes
- Lesser control over the cone
Acoustic Suspension
Acoustic suspension speakers first came into use in the 1950s. They were seen as the most accurate loudspeaker designs at the time. The enclosure is still quite popular to date. Many people often confuse an acoustic suspension system with an infinite baffle. The infinite baffle is a larger speaker, as the name suggests. It also produces deeper bass. Acoustic suspension systems use a relatively smaller enclosure which tends to have a larger resonant frequency than the infinite baffle.
Modern acoustic suspension speakers work at a resonance frequency of about 3 Hz. This means that the vibrations from the floorboards will be cut off from reaching the speaker. The same case applies to harder floors. An acoustic suspension is highly unlikely to rattle against the vibrations generated at high frequencies. This makes it your perfect candidate for all floor surfaces, whether it’s on a soft carpet or a tiled floor.
How Does An Acoustic Speaker Work?
An acoustic suspension subwoofer creates air pressure inside the enclosure. By increasing the air pressure inside the cone, the diaphragm moves linearly. In simple terms, the air cushion inside the enclosure restores the cone and acts as the main suspension for the speaker. The speaker elements move freely inside the cushion, producing very little to almost no heat. As a result, the speaker does not overheat, nor does its impedance.
Acoustic suspension speakers for sale usually come in smaller boxes. However, this means that they have to drain more power into the bass.
Pros
- High accuracy at all frequencies
- Less distortion at higher volume
- Tighter bass spikes
Cons
- Lesser efficiency over tuning frequency
- The system can be overdampended, giving the instruments unrealistic sounds
You should never use an acoustic suspension speaker in an unsealed cabinet. Without an enclosure, the mechanical suspension is too weak to remain in position. It needs an air cushion for extra support. Without it, you risk damaging the speaker.
What Is The Difference Between Bass Reflex And Acoustic Suspension?

The bass reflex enclosure remains the most popular of all time. People love it for its excellent bass response and high output. However, there are reasons why people go for acoustic suspension while others prefer bass reflex systems.
Bass extension – This is a system’s ability to play low notes. Generally, bass reflex systems are more efficient when it comes to bass extension. However, the bass roll off begins somewhere between 24dB/octave. On the other hand, the sealed speaker starts to roll off at 12dB/Octave. This is a much more gentle roll-off compared to the bass reflex enclosure.

Distortion – Bass reflex systems are prone to more distortion, especially from the ports. But thanks to technology, research, and advanced manufacturing, this should no longer be a problem. On the other hand, acoustic suspension systems have better dampening, which reduces distortion.
Sizes – Acoustic suspension types come in smaller boxes. They fit perfectly in smaller rooms. However, bass reflex systems come in much larger boxes. They are ideal for bigger rooms for spacing reasons.
Bass Reflex vs Acoustic Suspension FAQs
Although bass reflex systems are far more popular, there’s no right or wrong choice. It all boils down to what you want your system to do. Do you prefer loud sound or accurate audio? But before making your decision, here are the most frequently asked questions about the bass reflex vs acoustic suspension;
- Bass reflex vs sealed. Which one is better? – Both systems have their advantages and disadvantages. In the end, it depends on what you want from yours. Loudness or accuracy? Would you like big or small enclosures? Answer these questions to make the right decision.
- Is bass reflex good? – Bass reflex is deemed more efficient than an acoustic suspension because it allows bass extension at a higher volume. On the other hand, an acoustic suspension lowers the bass distortion. It also has a low resonance frequency.
You may also like learn Which Helps in Getting Better Sound? Read: Digital Amp vs. Analog Amp

