Connecting a speaker to an amplifier is generally not a difficult task, and most people with basic knowledge of audio equipment and wiring can do it themselves. There are several different methods of connecting a speaker to an amplifier, and the choice of method can have an impact on the sound quality and performance of the system
Bi-amping and bi-wiring are two of the most common methods of connecting a speaker to an amplifier. The two terms are often confused because both involve using multiple speaker cables to connect a speaker to an amplifier or an AV receiver. However, the two are totally two different concepts.
In this article, we’ll cover the difference between bi-amping and bi-wiring and the impact of each on your sound system.
Continue reading!
What is Bi-amping?
Bi-amping is a technique of connecting a speaker to two audio amplifier channels, with each channel dedicated to a specific frequency range of the speaker. For example, one channel can be used to power the low-frequency driver, and another channel can be used to power the high-frequency (tweeter) driver.
By using a separate audio channel for each frequency range, bi-amping is designed to provide more power and control over the sound. This often results in improved sound quality, greater dynamic range, and reduced distortion. Bi-amping can also allow for better speaker matching, as each channel can be specifically chosen to match the frequency range of the driver it is powering.
How Bi-amping Works
As we have stated, bi-amping works by using two separate amplifier channels to drive different frequency ranges of a speaker. Ideally, the audio signal is first split into separate frequency bands using a crossover network. The crossover is responsible for dividing the audio signal into two or more frequency ranges, with each range being sent to a different amplifier channel.
For example, the low-frequency range is often sent to the amplifier channel dedicated to driving the woofer, while the high-frequency range is sent be sent to the channel dedicated to driving the tweeter. By using a separate channel for different frequency ranges, each channel can be optimized to handle the specific requirements of that frequency range.
Generally, the channel dedicated to the low-frequency range is designed to deliver high amounts of power and handle the large excursions required by the woofer. On the other hand, the amplifier dedicated to the high-frequency range is designed to deliver low amounts of power and handle the delicate and nuanced sounds produced by the tweeter.
Bi-amping can provide several benefits over traditional speaker setups. First off, it can result in improved sound quality, greater dynamic range, and reduced distortion. It also allow for better speaker matching, as each amplifier channel is specifically chosen to match the frequency range of the driver it is powering.
What is Bi-wiring?
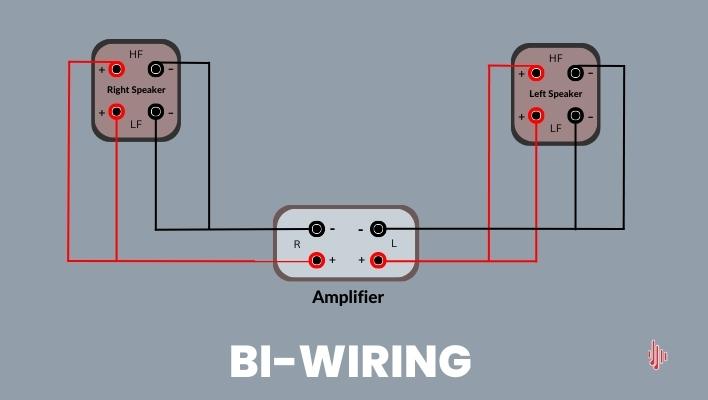
Bi-wiring is a speaker configuration technique that involves using two sets of speaker wires and connectors to connect a single speaker to a power amplifier or receiver. Instead of using a single pair of wires to connect the amplifier to the speaker’s crossover, bi-wiring separates the signal into two separate frequencies bands and sends them through separate sets of wires.
The idea behind bi-wiring is that by separating the frequencies, each set of wires can handle a narrower range of frequencies, resulting in a more accurate and clearer sound. In theory, this can improve the overall sound quality of the speaker system.
Bi-wiring requires a speaker that has two sets of binding posts, one for the high-frequency driver and one for the low-frequency driver. It also requires an amplifier or receiver that has two sets of speaker outputs for each wire.
However, the benefits of bi-wiring are highly debated, and some audiophiles believe that the difference in sound quality is negligible or non-existent. Additionally, not all speakers are designed to be bi-wired, and attempting to do so on a speaker that is not designed for it can compromise the speaker’s performance.
How Bi-wiring Works
Bi-wiring works by using two separate sets of cables to connect a single pair of speakers to an amplifier or receiver. One set of cables is used for the low frequencies (bass driver) while the other set is used for the high frequencies, usually the tweeter or mid-range drivers.
When a signal is sent from the amplifier or receiver to the speakers, the signal is split into two separate paths at the binding posts on the speaker. One path carries the low-frequency signals to the bass driver, while the other carries the high-frequency signals to the tweeter and mid-range drivers.
Ideally, bi-wiring helps to separate the signal paths for the different frequencies, which reduces interference and crosstalk between them, resulting in a clearer, more accurate sound. Additionally, bi-wiring can reduce the load on the amplifier or receiver by allowing it to drive the speaker drivers separately, thereby improving the overall performance of the audio system.
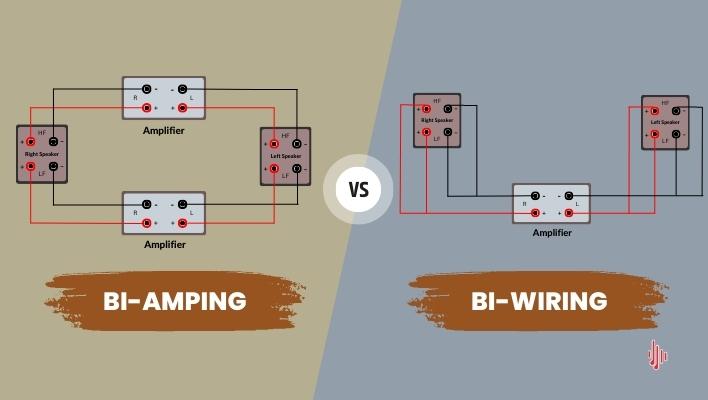
Bi-amping vs Bi-wiring- Different or Same?
Bi-wiring and bi-amping are by far the most common methods of connecting speakers to an amplifier or receiver, and they each have their own benefits and drawbacks. As such, it’s important to carefully consider the pros and cons of each before making a decision.
The main difference between bi-amping and bi-wiring is the way in which the speaker cables are connected to the speaker terminals. While both bi-wiring and bi-amping involve using separate cables for the high and low-frequency drivers of a pair of speakers, bi-amping requires two separate amplifier channels, whereas bi-wiring only requires one channel.
Bi-amping separates the signal into two or more frequency bands, allowing each driver to receive only the frequency range that it is designed to handle. This often results in improved sound quality and clarity. In addition, bi-amping allows for greater control over the individual drivers, which can help reduce distortion and improve overall sound quality.
Bi-amping may be a good option if your speakers have separate drivers for the low and high frequencies. Bi-amping is also ideal if you have a larger room or a more demanding listening environment where more power and control over the individual frequency ranges would be beneficial.
On the other hand, bi-wiring allows for greater flexibility in speaker placement, as it allows for separate connections to the low and high-frequency drivers. Overall, bi-wiring may be the best choice if your speakers have separate binding posts for the low and high frequencies.
It is also the best option when you want to experiment with different cable types or configurations to see if they improve the sound quality or when you are not interested in the additional complexity of bi-amping.
Parting Shot!
Bi-amping is considered to be a more effective technique for improving sound quality, as it allows for more precise control over each driver and reduces intermodulation distortion between them. Bi-wiring, on the other hand, may provide some improvement in sound quality, but it’s not necessarily a guaranteed way to improve sound quality.
Ultimately, the best approach will depend on the specific equipment you’re using and the preferences of the listener. That said, it may be worth experimenting with both bi-amping and bi-wiring to see which one provides the best sound quality for your particular setup.
